Jan Van Eck told CoinDesk TV’s Jen Sanasie that not hearing back from the SEC is a sign that ETH exchange-traded funds likely wont make the May deadline.
Ethereum Hit by ‘Blobscriptions’ in First Stress Test of Blockchain’s New Data System
Ethereum fees for “blobs” – the blockchain’s new dedicated class of cheaper data storage – spiked Wednesday after a project called Ethscriptions created a new way of inscribing data, known as “blobscriptions.”
Developers Upload Script of Jerry Seinfeld’s ‘Bee Movie’ on Ethereum as Gas Fees Plunge After Dencun
Copying and pasting the Bee Movie script is a niche internet meme that originated on Tumblr and quickly spread to Reddit, YouTube, Facebook, and other social media platforms.
Ethereum Activates ‘Dencun’ Upgrade, in Landmark Move to Reduce Data Fees
A key element of the upgrade is to enable a new place for storing data on the blockchain – referred to as “proto-danksharding,” which gives room for a dedicated space that is separate from regular transactions, and at a lower cost.
Ethereum Blockchain Counts Down to ‘Dencun’ Upgrade, Set to Reduce Fees
The upgrade is designed to usher in a new era of cheaper fees for the growing array of layer-2 networks that operate on top of Ethereum.
Meme Coin Frenzy Drives Ethereum Network Fees to Nearly 2-Year High: IntoTheBlock
Ethereum network fees surged to nearly two-year highs, largely driven by the speculative frenzy with meme tokens such as PEPE, SHIB and FLOKI.
Uniswap Founder: Dapps Will Soon Handle Gas Fees On Behalf Of Clients
In comments likely to resonate with crypto fans, Hayden Adams, the founder of Uniswap, a leading decentralized exchange (DEX), predicts that network fees will eventually become a background expense for users, much like server costs are today for top centralized applications running on Amazon Web Service and other platforms.
Gas Fees Is A Major Pain Point, Mass Migration To Solana, Layer-2 Platforms
Taking to X, Adams envisioned a future where decentralized applications (dapps) seamlessly cover network fees on behalf of users. This approach, the inventor adds, aligns with how server costs are currently handled in the current setup, especially among operators of common applications like X or Facebook.
Server costs are often considered a hidden expense in the overall business model. However, this can cost millions of dollars monthly, depending on the app’s popularity.
Presently, the dream of low-fee transactions remains out of reach for some blockchains, particularly Ethereum, the dominant platform for smart contracts. Ethereum is a legacy blockchain that recently shifted from a proof-of-work to proof-of-stake consensus.
However, while this was a major shift, the network still struggles with scaling challenges. At optimum, Ethereum can only process 15 transactions every second. Comparing this with current demand only means “gas fees” must be high to incentivize the validator to include transactions in the next block.
This high “gas fee” continues to be a major pain point, leading some projects to migrate to alternative networks with faster transaction speeds and lower fees. Solana, a high-throughput blockchain, and layer-2 scaling solutions like Arbitrum have emerged as popular destinations for these migrating projects. This trend is particularly evident with the recent surge of meme coins like BONK and WIF, which have seen significant growth on Solana.
Unlike Ethereum, Solana and layer-2 platforms relying on Ethereum for security boast higher throughput and negligible gas fees. Accordingly, more meme coin projects are launching on these networks. Here, users can transact without considering the implication of gas fees. In recent weeks, top meme coins, besides PepeCoin (PEPE) or Dogecoin (DOGE), have been launching on Solana.
Ethereum Is Working On Scaling
Ethereum will implement the Dencun Upgrade in mid-March to combat its scaling woes. The update aims to reduce costs for users interacting with layer-2 solutions significantly. However, this upgrade is just one of the many Ethereum developers plan to implement over time.
Eventually, the proof-of-stake network aims to scale processing speeds, allowing it to execute millions of transactions every second through innovations like Sharding.
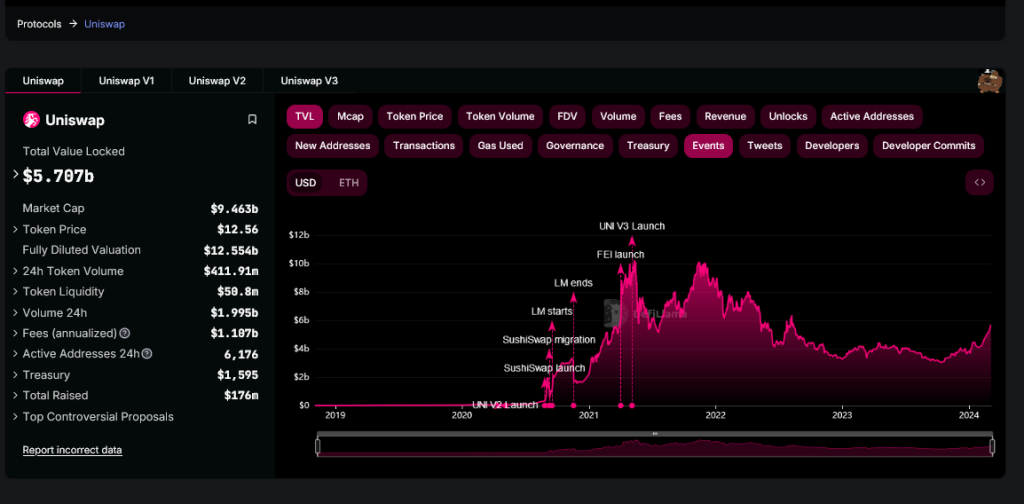
Uniswap continues to lead in popularity, looking at assets under management. So far, Uniswap developers have deployed its solution across other blockchains and layer-2 options, including Arbitrum and the BNB Chain.
Ethereum’s Vitalik Buterin Proposes Gas Limit Increase
Ethereum’s gas limit refers to the maximum amount of gas that can be expended in an individual block. A limit increase could improve network capacity and potentially reduce costs for users.
Immutable's zkEVM to eliminate Web3 gaming gas fees

Immutable’s blockchain protocol will allow the game studio to cut out gas fees for users, which is widely cited as a significant barrier to Web3 gaming adoption.
Immutable's zkEVM to eliminate Web3 gaming gas fees

Immutable’s blockchain protocol will allow the game studio to cut out gas fees for users, which is widely cited as a significant barrier to Web3 gaming adoption.
Immutable's zkEVM to eliminate Web3 gaming gas fees

Immutable’s blockchain protocol will allow the game studio to cut out gas fees for users, which is widely cited as a significant barrier to Web3 gaming adoption.
DeFi gathering momentum, Ethereum Gas Fees Rising: Why Is Uniswap (UNI) Stuck?
Decentralized finance (DeFi) activity on Ethereum is picking up momentum based mainly on how gas fees have been trending in the first three weeks of November, data from Kaiko shows. Even so, despite Uniswap (UNI) spearheading the revival, looking at the gas attributed to its activities over this period, UNI prices remain stagnant below $5.6, with bulls failing to edge higher, breaking to new 2023 highs.
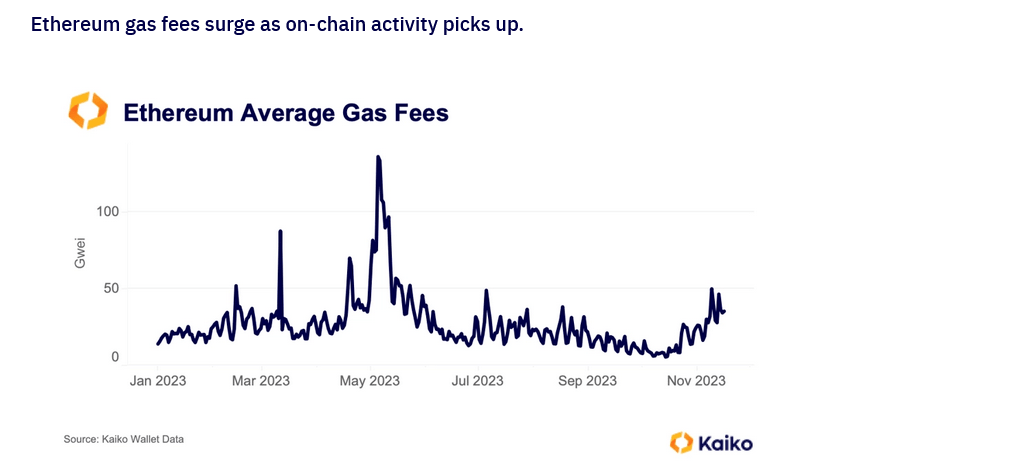
Ethereum Gas Fees Rising, DeFi Revival?
According to Kaiko, a blockchain analytics platform, the average gas fees on Ethereum hit multi-month highs last week. The platform expressly notes that the primary driver has been Uniswap’s activities, reading from the rising transaction volumes from meme coins, including GROK. This, in turn, pushed block space demand higher, increasing gas fees.
Gas fees remain volatile but generally higher in the first three weeks of November. As of November 20, Ycharts data shows that the average cost of sending a transaction stood at 45.13 Gwei, nearly 100% from November 19, when it was at 24.84 Gwei. This is a significant jump from 17.66 Gwei in late October 2023.
Gas fees and how ETH and DeFi token prices react are directly correlated as DeFi and other on-chain activities like non-fungible token (NFT) minting and trading rise; gas fees usually expand in trending markets.
Accordingly, the recent expansion in gas fees could suggest that the markets could be preparing for a leg up, and tokens of critical protocols, including Uniswap or Aave, could benefit.
DeFi TVL Rising, But Uniswap Is Stuck Below $5.6
As of writing, the total value locked (TVL) across all DeFi protocols stands at over $46.6 billion as of November 21, according to DeFiLlama. This increase is nearly $5 billion more than in early November and up from $37 billion in mid-October.
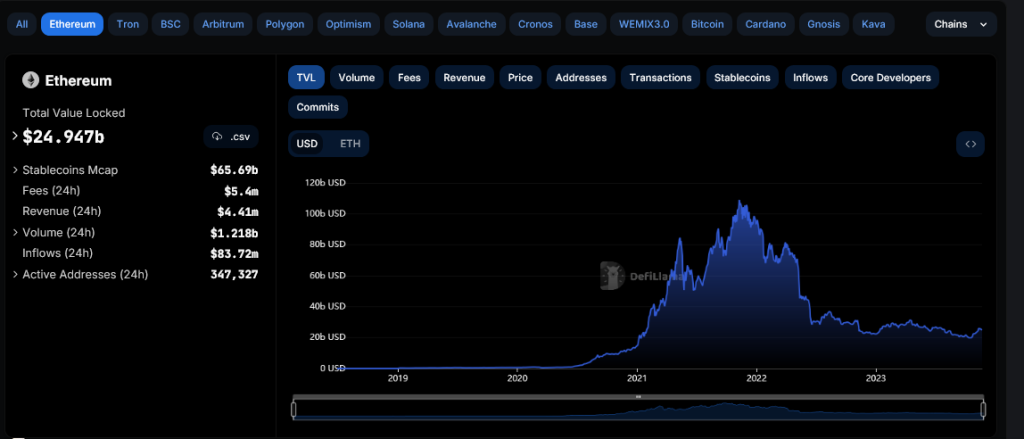
Ethereum remains a choice platform for deploying DeFi apps despite the relatively gas fees pinned to mainnet scaling challenges. The pioneer smart contract blockchain manages $25.4 billion in TVL, whereas Uniswap is one of the largest protocols with $3.216 billion in TVL.
UNI prices are up 30% from mid-October when writing on November 21. However, bulls have been unable to break above the November highs at around $5.6. From the daily chart, trading volume, and thus participation, has been tapering even though prices have been edging higher.
This formation suggests that the uptrend was behind low momentum and sustainability. Technically, there could be more gains if there is a solid close above November highs with expanding volumes. In that case, UNI could expand, retesting 2023 highs of around $7.2.
Ethereum, Bitcoin users reignite scalability debate as gas fees surge

Ethereum gas fees reportedly breached the $200-mark for certain high-priority transactions in the last 24 hours.
66% Of Top Smart Contracts On Base Have One Big Problem
14/21, or 66%, of the top gas-consuming smart contracts on Base, a layer-2 platform for building and deploying smart contracts, are unverified. According to Token Terminal data on October 24, the same contracts are some of the most actively used, reading from gas fee trends over the last month.
Friend.tech Leads The Gas Race On Base
Base is a layer-2 scaling solution and one of OP Mainnet and Arbitrum’s competitors. The platform relies on the Optimistic Rollup technique, allowing transactions to be batched off-chain before being confirmed on the mainnet. This is the same approach competitors, including Arbitrum and OP Mainnet, adopted.
As of October 24, the most gas-consuming protocol already labeled and known to be deployed from a given developer is Friend.tech. Still, the developer remains anonymous.
The decentralized social media protocol allows users to buy and sell keys to each other’s X accounts. In this way, trading parties can access exclusive in-app chatrooms and content by a given user.
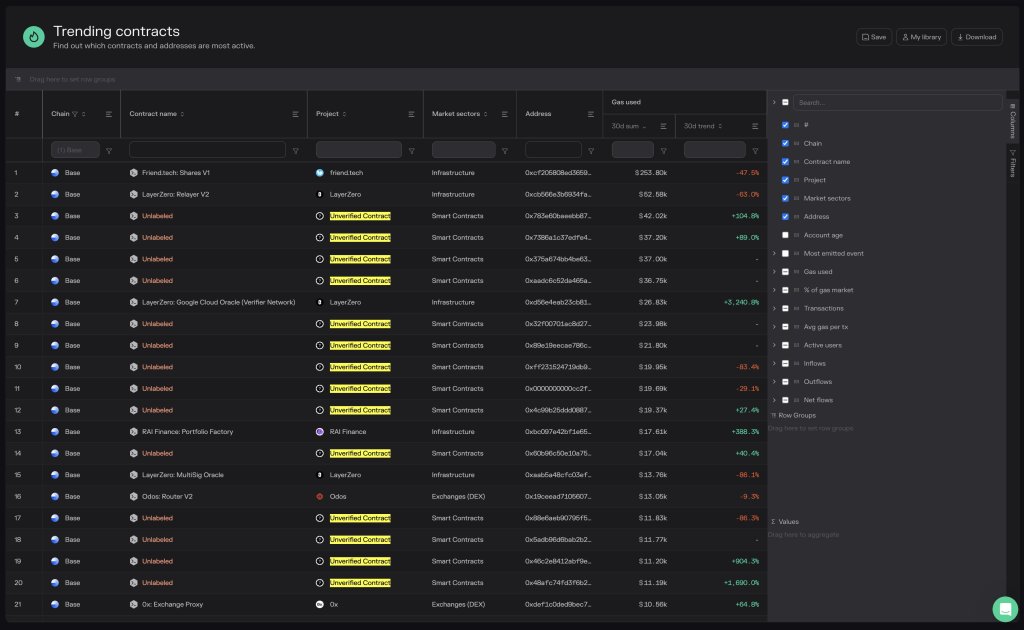
By deploying on Base, Friend.tech users enjoy lower trading fees than they would have launched on the mainnet. Beyond fees, the protocol can also scale since the layer-2 solution can handle higher throughput than the mainnet.
In the last month, Friend.tech generated over $253,000 in gas fees. The execution fee, often known as layer-2 fee, on Base, which uses Optimism, is set by the network and is flat.
The fee prevents users from spamming the network and rewards nodes that prove all transactions submitted on the platform. The other fee is the approximate for confirming the same transaction batch on the mainnet. This fee is generally higher than the execution fee.
The Case Of Popular But Unverified Smart Contracts
While gas fees generated by Friend.tech is over $253,000, it is down over 47% in the last month. This could suggest that trading activity fell since the fee generated by a network is directly proportional to how frequently it is used.
Friend.tech fees, when writing, remain suppressed, underperforming the activity of unverified smart contracts, looking at fees generated over the last month. Over the previous 30 days, one unverified contract has seen a 104% increase in trading fees, reaching $42,000. Another contract has increased by 1,690%, exceeding $11,000 in the same period.
As the name suggests, these unverified codes have yet to be confirmed by a third party. This can mean there is no guarantee that the same developer built and deployed code on Base. At the same time, the code might contain malicious code that could steal from addresses it interacts with.
Circle to Let Merchants Pay for Customers’ Gas Fees With Web3 Wallet Upgrade
Southeast Asian super app Grab is currently piloting the “Gas Station” to cover gas fees for its Singaporean users if they use NFT vouchers.
The Protocol: Friend.tech Fades as Crypto Craze, but Ethereum Is Scaling
This week in blockchain tech: Polygon’s new “chain development kit,” Farcaster’s move to Optimism, Shibarium’s return and Interlay’s new Bitcoin layer-2 network, and Pancake Swap expands to Consensys’s Linea.
Ethereum Handled Friend.tech Frenzy Without ‘Gas Fee’ Spike. Why That’s a Big Deal
Friend.tech, Crypto’s latest fad, didn’t drive up congestion and fees on Ethereum the way frenzies have in the past – possibly a sign that the blockchain’s efforts to scale by fostering supplemental “layer-2” networks, like Coinbase’s new Base, are bearing fruit.
Crypto Assets Flow From Ethereum To BSC, Are Users Escaping High Gas Fees?
There is a substantial flow of assets from Ethereum to the Binance Smart Chain (BSC), according to data from Cryptoflows.
Migration From Ethereum To BSC
The shift to move assets from the legacy smart contracting network could be driven by the desire to escape high gas fees.
For every transaction executed on public ledgers like Ethereum and BSC, a fee is paid. In Ethereum, gas fees remain higher, especially for users deploying smart contracts.
Analysis of the latest gas fee trends on Etherscan indicates shows that network fees have been fluctuating, and generally higher in the past weeks. As of May 17, Gas fees stood at 43 gwei or roughly $1.59 for simple transfers.
Meanwhile, BscScan data shows that users have to pay 3 gwei for transfers, regardless of the urgency of the transaction.
The difference in gas fees between Ethereum and BSC, when analyzed in USD terms, is apparent and could explain why users are seeking alternatives, moving assets from Ethereum to alternative blockchains like BSC that offer lower Gas fees.
Is PEPE FOMO The Reason?
The recent surge in Ethereum gas fees can be attributed, in part, to the hype surrounding the PEPE, a meme token. With PEPE spurring demand and forcing on-chain activity higher, Ethereum gas fees rose in tandem. According to Y-Charts, Gas fees on Ethereum increased from $43 on April 22 to $155 as of May 5, 2023.
The unprecedented demand for PEPE due to the fear of missing out (FOMO) coincided with the near-exponential increase of fees from the last week of April to early May.
This spike highlighted the scalability challenges faced by Ethereum during periods of increased activity.
Fluctuating Gas fees, depending on network activity, is primarily one of the reasons why developers are looking to integrate long-lasting solutions, including on-chain and off-chain scaling methods.
According to the roadmap, Ethereum will introduce Sharding, where the network will be broken into portions called “shards”.
Shards are sub-networks that will form part of the whole of the Ethereum blockchain. Each Shard will process transactions independently but remain connected to other shards. In this system, Ethereum developers hope to scale transaction processing throughput on-chain, lowering fees. Shards remain an idea and are being studied.
Given this, layer-2 scaling options are gaining traction as a means of improving scalability by re-routing transactions to an off-chain platform, relieving the underlying blockchain, and reducing processing fees.
L2Beat currently shows that there are over 20 layer-2 scaling options aiming to scale the mainnet. Arbitrum and Optimism, two of the most active general-purpose platforms for deploying smart contracts and decentralized applications are the most active. The two, Optimism and Arbitrum, control over $7.5 billion of assets as measured by total value locked (TVL).
Optimism will release “bedrock,” via a hard fork in early June 2023. This upgrade aims to enhance scalability, improve transaction speeds, and reduce gas fees on the off-chain solution. With these improvements, Optimism hopes to carve out a larger market share, pushing its TVL higher.
Anchorage Digital opens up DeFi voting for custody clients

Anchorage joins AAVE, Lido and BitDAO in adopting the off-chain voting platform Snapshot.
Worth it? Trader spends $120K on gas buying $155K worth of a memecoin

A user spent an additional 76% of their total purchase price in gas fees on a single memecoin trade.