In the rapidly evolving landscape of blockchain technology, Neon EVM, a smart contract on Solana (SOL) has emerged as a frontrunner by introducing a landmark parallel processing architecture on its mainnet.
This approach has enabled Neon EVM to achieve an increase in performance, scalability, and efficiency, according to a press release share with NewsBTC.
Neon EVM Dominates Transaction Processing
Neon EVM, the first parallel Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) on mainnet, has achieved a record-breaking 730 Transactions Per Second (TPS) on its mainnet. Notably, this is the first time such high tps has been achieved on an EVM mainnet.
The milestone was reached on December 16, 2023, when Neon EVM’s mainnet showcased its transaction processing capabilities. While many blockchains demonstrate high tps on testnets, Neon EVM’s has standout by improving its scalability.
Neon EVM, which went live on the mainnet in July 2023, operates as a fully Ethereum-compatible environment on the Solana blockchain. Since its launch, Neon EVM has garnered investor interest, resulting in multiple listings on platforms such as ByBit, Crypto.com, and Gate.io.
Given these developments, the utility token NEON has experienced remarkable growth, with its value surging from $0.67 to $1.45 in just three days, representing a 116% increase.
Neon EVM’s success comes when there is growing interest in high-speed, parallelized processing blockchains. Currently, Neon EVM stands as the only parallel processing EVM live on the mainnet, showcasing its tps capabilities compared to other blockchain networks.
Outshining Ethereum’s Transaction Speed
The fundamental difference between Neon EVM and blockchains like Bitcoin and Ethereum lies in their transaction processing approach. While Bitcoin and Ethereum process transactions sequentially, Neon EVM allows for simultaneous processing of multiple transactions, facilitating increased throughput and reducing the likelihood of congestion during periods of high demand.
In a notable comparison, Neon EVM’s parallel processing architecture outperformed the combined tps of the entire Ethereum ecosystem on December 16, as reported by L2Beat.
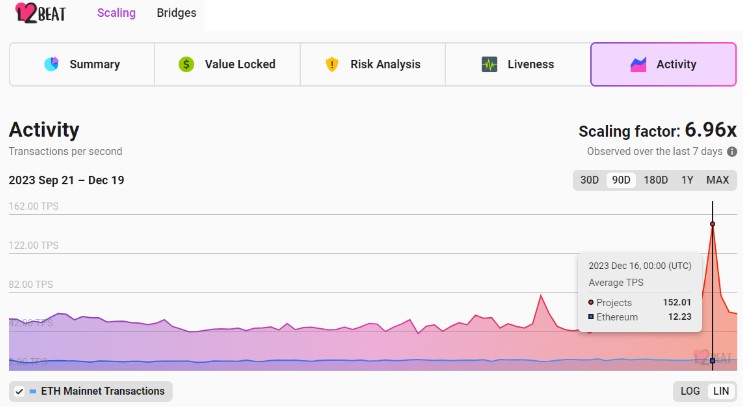
The project’s commitment to Ethereum compatibility on the Solana blockchain and its high-speed transactions and low-cost benefits positions Neon EVM as an interesting project as a new Bull Cycle emerges.
Layer 2 Scaling Solutions On The Rise
Polygon, the layer 2 scaling solution that operates alongside the Ethereum blockchain, has also demonstrated its transaction processing speed capabilities.
In a recent post on X (formerly Twitter), Sandeep Nailwal, the founder of Polygon, shared notable statistics highlighting the network’s performance. According to Nailwal’s post, Polygon’s Proof of Stake (PoS) chain seamlessly handled over 16 million transactions in a single day, showcasing its scalability and efficiency.
During the peak period, the Polygon PoS chain achieved a throughput of 255 tps. This figure is approximately 2-3 times higher than the combined throughput of the entire Ethereum ecosystem.
Moreover, the validators on the Polygon network generated approximately 1 million in transaction fees in a single day, reflecting the network’s high level of activity. However, it is worth noting that gas fees experienced a spike during this period, which is a broader issue impacting the entire Ethereum ecosystem.
In terms of rewards for validators, the block rewards on the Polygon network amounted to over 155,000 MATIC tokens. This translates to substantial revenue for validators, totaling around 1.2 million in a single day. These rewards incentivize validators and contribute to the overall security and stability of the PoS chain.
The spike in transactions in both of these Layer-2 networks showcase the growing importance of scalability solutions. In the coming months, hundred of new users could onboard the crypto market via either of these solutions hinting at a potential benefit for their underlying tokens.
Featured image from Shutterstock, chart from TradingView.com