It’s the year 2045. Digital assets move at the speed of light. AI agents interact millions of times a second, using bitcoin as a base currency. Bitcoin is now a $200 trillion asset class, a settlement layer for the AI Age of the Internet.
This is the future imagined by bitcoin evangelist Michael Saylor, the executive chairman of Strategy (MSTR). Saylor pioneered the bitcoin corporate treasury – turning his flailing software firm into a Nasdaq-listed $85 billion leveraged bitcoin powerhouse.
CoinDesk recently sat down with Saylor, Bitcoin’s ultimate maximalist, for a two-hour interview to break down his vision for global bitcoin domination.
Since the election of U.S. President Donald Trump, bitcoin has maintained a 26% gain, peaking at a $2.1 trillion market cap, and touching a January all time high of $109,000. Strategy, a Wall Street proxy for bitcoin, remains strong with about a 50% gain, despite dropping approximately 30% from November highs amid a broader decline in U.S. equities, the U.S. 10-year Treasury yield, and oil.
The United States went from regulating crypto by enforcement and covertly de-banking digital asset firms, dubbed “Operation Chokepoint 2.0” by the industry, to declaring that the U.S. will become a bitcoin superpower and the crypto capital of the world. For Saylor, the sea change means doors that were previously closed are opening. Governments and traditional institutional investors around the world that used to be afraid of engaging with digital assets are now curious.
Saylor said he is fielding invitations to speak at all the elite gatherings: South America’s 100 wealthiest families, Middle Eastern sovereign wealth funds, Morgan Stanley’s prestigious tech conference, CPAC, and the White House. He has gone from encouraging corporations to adopt bitcoin treasuries to advising nation states on establishing strategic bitcoin reserves.
Bitcoin has reached “escape velocity,” he said, because once the U.S. government begins to acquire it aggressively, the U.S. will become a beneficiary and force every country to adopt bitcoin as the global capital.
“It becomes a fait accompli,” said Saylor. “It’s one of those geopolitical moves that when you embrace the network, you force all of your allies first to adopt it, and then all your enemies have to adopt it.”
U.S. Bitcoin Strategic Reserve
President Trump’s executive order to establish a U.S. Bitcoin Strategic Reserve represents a milestone in realizing bitcoin’s manifest destiny. At one point, the U.S. held about 400,000 bitcoins, but sold half of it for proceeds of $366 million. Trump’s crypto czar David Sacks lamented that the cost to American taxpayers for selling this bitcoin prematurely is $17 billion at current market value.
The executive order directs the Secretary of the Treasury to never sell the United States’ bitcoin and to develop budget neutral ways to acquire more bitcoin. It further directs the creation of a digital asset stockpile, a portfolio of seized crypto assets that can be managed and rebalanced as necessary.
At President Trump’s White House Digital Assets Summit on March 7, Saylor proposed that the U.S. acquire 5%-25% of the total bitcoin supply by 2035 that could generate an estimated $100 trillion in economic value by 2045.
When asked about this proposal, Bo Hines, Executive Director of the Presidential Council of Advisers for Digital Assets, told CoinDesk the Trump administration wants the U.S. to acquire as much bitcoin “as we can possibly get” and is considering various creative methods, including Senator Cynthia Lummis’ (R-Wyo) proposal to use Federal reserve earnings and gold certificates to buy bitcoin.
As the U.S. embraces bitcoin, worldwide banks will inevitably follow.
“ Pandora’s box has been opened,” said Saylor. “When bitcoin spreads… and there’s a trillion dollars of digital capital in the banking system, it won’t just be in the U.S. It’s a virus. And so the virus spreads. And in this case, that means you’re going to have hundreds of thousands of banks and trillions of dollars that are held by a billion people.”
‘Thermodynamically Sound’ Money
Michael Saylor was born in Lincoln, Nebraska. He grew up on Air Force bases across the Midwest, as well as in Japan and New Zealand. An Air Force scholarship sent Saylor to the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, where he obtained dual degrees in aeronautics, astronautics, and the history of science. A literal rocket scientist, Saylor’s systems mindset attracted him to bitcoin’s “thermodynamically sound” design.
After serving as an Air Force Reserve captain, Saylor co-founded MicroStrategy in 1989, a software firm that rode the dot-com bubble, until Saylor and two other MicroStrategy executives were embroiled in an accounting fraud scandal in 2000. Eventually, they settled with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission for about $11 million.
At MicroStrategy, Saylor invented over 48 patents and deployed dozens of business ideas. Some succeeded, most of them failed. Saylor said the irony is that his greatest success was somebody else’s idea. Satoshi Namamoto, the pseudonymous creator of Bitcoin, created “digital gold” that Saylor discovered while under lockdown during the Covid-19 pandemic. He grabbed onto it out of desperation, preferring MicroStrategy to have a quick death over a slow one if it failed.
In July 2020, MicroStrategy began to steadily and continuously purchase bitcoin through cash flows, equity and debt, basically any way it could. It climbed the highs of the 2021 bull run and withstood the impairment charges of the 2022 crypto winter. By 2024, the Bitcoin corporate treasury strategy emerged battle tested. It survived its first crypto market cycle and the Trump bump catapulted MicroStrategy from a $1 billion to a $100 billion market cap company.
“[Bitcoin] became an opportunity,” said Saylor. “Then it became a strategy, and then all of a sudden in the past 12 months, we realized it was a really good business.”
From MicroStrategy to Strategy
MicroStrategy, rebranded and doing business as “Strategy,” proved to be an incredibly desirable stock for institutional investors wanting exposure to the volatile ups and downs of bitcoin. In December, Strategy was admitted to the Nasdaq 100. It is now eyeing membership to the S&P 500, which would spark an additional tidal wave of public market access.
To generate positive momentum, Strategy is laser-focused on raising capital to buy more bitcoin through a plethora of fixed income securities, creating a casino of financial products for traders addicted to bitcoin’s volatility. By constantly weighing market conditions, tweaking yield parameters and conversion factors, Strategy has engineered “intelligent leverage” designed to lure demand and ensure each successive series of securities amp each other up in an endless positive feedback loop.
“If you were to say, it sounds like financial engineering, it absolutely is financial engineering,” said Saylor. “ It creates more pressure to drive up the price of bitcoin, which drives up the price of MSTR, which drives up the leverage of MSTR, which drives up the value of the options, which drives up the demand for the equity, which drives up the demand and the value of the [convertible bonds], which drives up the price of and the demand for the preferred [shares].”
Strategy has raised approximately $33 billion to purchase half a billion bitcoins through this financial engineering. That has ignited online debate regarding Strategy’s ability to pay out dividends or bond maturities if markets sour or it cannot raise fresh capital. The money likely won’t come from existing company cash flows: Strategy’s software profits are negligible; in 2020-2023, they were negative, according to MarketWatch data.
All of this keeps Saylor up at night. So, Strategy is keeping all of its options open.
“ When the equity capital markets give us a massive premium, we’ll sell the equity,” said Saylor. “If we get too levered, we will de-lever. If we feel that the capital markets aren’t really favorable to sell any securities, we’ll just stop and wait.”
Last week, Strategy brought its bitcoin holdings above 500,000 tokens by purchasing an additional 6,911 bitcoins for $584 million, using proceeds from the sale of MSTR common stock. They further announced their new STRF perpetual offering raised $711 million to buy more bitcoin, when its initial goal was to raise $500 million.
This latest series of preferred stock differs from the original STRK offering in that it comes with a higher coupon (10% versus 8%) and has no common share conversion provision. Spelled out in the prospectuses of both offerings are risk factors that include no obligation to pay accumulated dividends “for any reason.”
Strategy has also eliminated any collateralized debt and therefore liquidation risk of the company’s bitcoin assets.
”We’ve built an indestructible balance sheet. Bitcoin could trade down 99%. There’s no margin call coming. The instruments that are constructed don’t have Bitcoin pledged as collateral,” said Saylor.
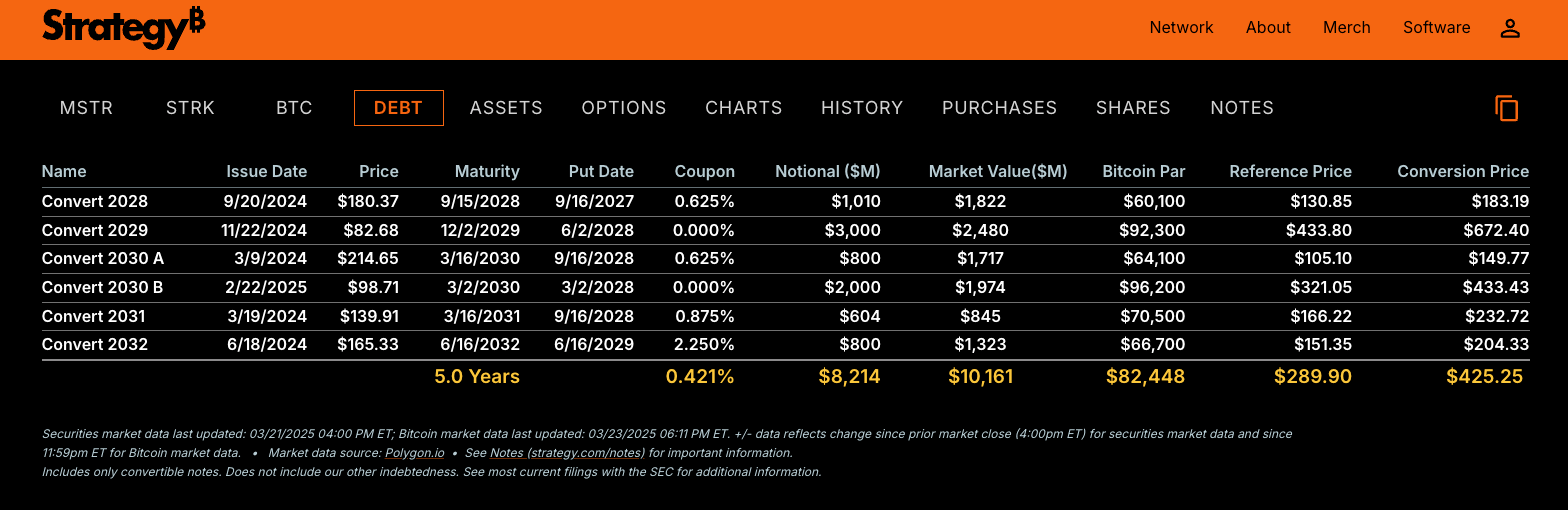
Ultimately, the dates to watch are when Strategy’s loans to bondholders become due. The first “put date” is September 16, 2027. If Strategy fails to incentivize bondholders to convert their bonds to MSTR stock or persuade them to await principal repayment the following year, these bondholders might demand Strategy buy back their $1.8 billion loan in cash. If the markets are still hungry for bitcoin exposure, it will be easier to raise capital and pay back investors. If there is a market downturn, and the Wall Street spigot runs dry, Strategy may have to consider selling its bitcoin or default.

‘Economic immortality’
But Saylor said Strategy, like the U.S. government, will “never sell” its bitcoin. He’s bet everything on BTC price going up forever, and the sovereignty, sound money, freedom, and property rights idealized by the community.
Before he dies, Saylor may burn bitcoin rather than give his assets away. That would be a “more ethically proper, ethically sound form of charity” and would bestow “economic immortality.”
“ If I believe that and I burn those keys, then I have made everybody in the [Bitcoin] network that much richer and more powerful forever,” said Saylor. “We’re all in it together, from now to eternity. So yeah, that’s my legacy.”